Aquatic invasive species (AIS) are non-native species introduced to an aquatic ecosystem that causes environmental and/or economic harm. AIS can cause issues that impact our lakes, streams, and wetlands and are increasingly the focus of Watershed Council monitoring and management programs. Knowing how to identify AIS, how they got here, and what you can do to help prevent them from spreading is important.
Some invasive species are legally designated by the State of Michigan as either “prohibited” or “restricted.” If a species is prohibited or restricted, it is unlawful to possess, introduce, import, sell or offer that species for sale as a live organism, except under certain circumstances. Michigan’s Natural Resources Environmental Protection Act (Part 413 of Act 451) established the list of prohibited and restricted species, which is regularly amended by Invasive Species Orders. Other Michigan laws may apply to harvesting, possessing or selling regulated and unregulated species.
Credit: Prohibited and restricted. (n.d.). Retrieved March 21, 2023, from https://www.michigan.gov/invasives/id-report/prohibitedrestricted
Watchlist
Invasive species on the watch list have been identified as posing an immediate or potential threat to Michigan’s economy, environment or human health. These species either have never been confirmed in the wild in Michigan or have a limited known distribution.
If you think you have found any of these species in Michigan, please report the occurrence via the methods given below by clicking on an individual species name.
Credit: Watch list. (n.d.). Retrieved March 21, 2023, from https://www.michigan.gov/invasives/id-report/watchlist
Prohibited
The term “prohibited” is used for species that are not widely distributed in the state. Often, management or control techniques for prohibited species are not available.
Restricted
The term “restricted” is applied to species that are established in the state. Management and control practices are usually available for restricted species.
Some invasive species are legally designated by the State of Michigan as either “prohibited” or “restricted.” If a species is prohibited or restricted, it is unlawful to possess, introduce, import, sell or offer that species for sale as a live organism, except under certain circumstances. Michigan’s Natural Resources Environmental Protection Act (Part 413 of Act 451) established the list of prohibited and restricted species, which is regularly amended by Invasive Species Orders. Other Michigan laws may apply to harvesting, possessing or selling regulated and unregulated species.
Credit: Prohibited and restricted. (n.d.). Retrieved March 21, 2023, from https://www.michigan.gov/invasives/id-report/prohibitedrestricted
Mobile Boat Washing
Tip of the Mitt Watershed Council has been running a Mobile Boat Washing Station Program since 2020. We use high-pressure, heated water to wash invasive plants and animals off boats and trailers. We visit various Northern Michigan lake landings and wash boats for free throughout the summer. The Mobile Boat Washing event calendar and more program information can be found here.
Guide to Our Invasive Species
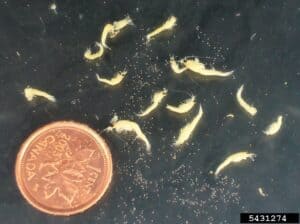
Bloody Red Shrimp
The bloody red shrimp is a mysid, a relative of the native Great Lakes opossum shrimp, Mysis relicta

Brazilian Elodea
Rapid growth leads to dense, monospecific mats on the surface of the water. These mats crowd out native

Water-primrose
Invasive water-primrose species are aquatic plants that can thrive and spread in shallow water areas including wetlands and

Curly-Leaf Pondweed
The origins of its introduction are unknown, but it is suspected that it was possibly imported as an

Eurasian Watermilfoil
Eurasian watermilfoil (Myriophyllum Spicatum) is a plant native to Europe and Asia that was first documented in North

European Frogbit
Hydrocharis morsus-ranae, better known as European Frogbit, is an aquatic, invasive species currently spreading throughout the Great Lakes

Flowering Rush
Flowering rush originated in Eurasia but can now be found throughout the Midwest, including in Southern Michigan, and

Giant Hogweed
Giant Hogweed is a Federally listed noxious weed. Its sap, in combination with moisture and sunlight, can cause

Golden Mussel
Golden Mussel is native to Chinese and south-eastern Asian rivers and creeks. It became established in Hong Kong
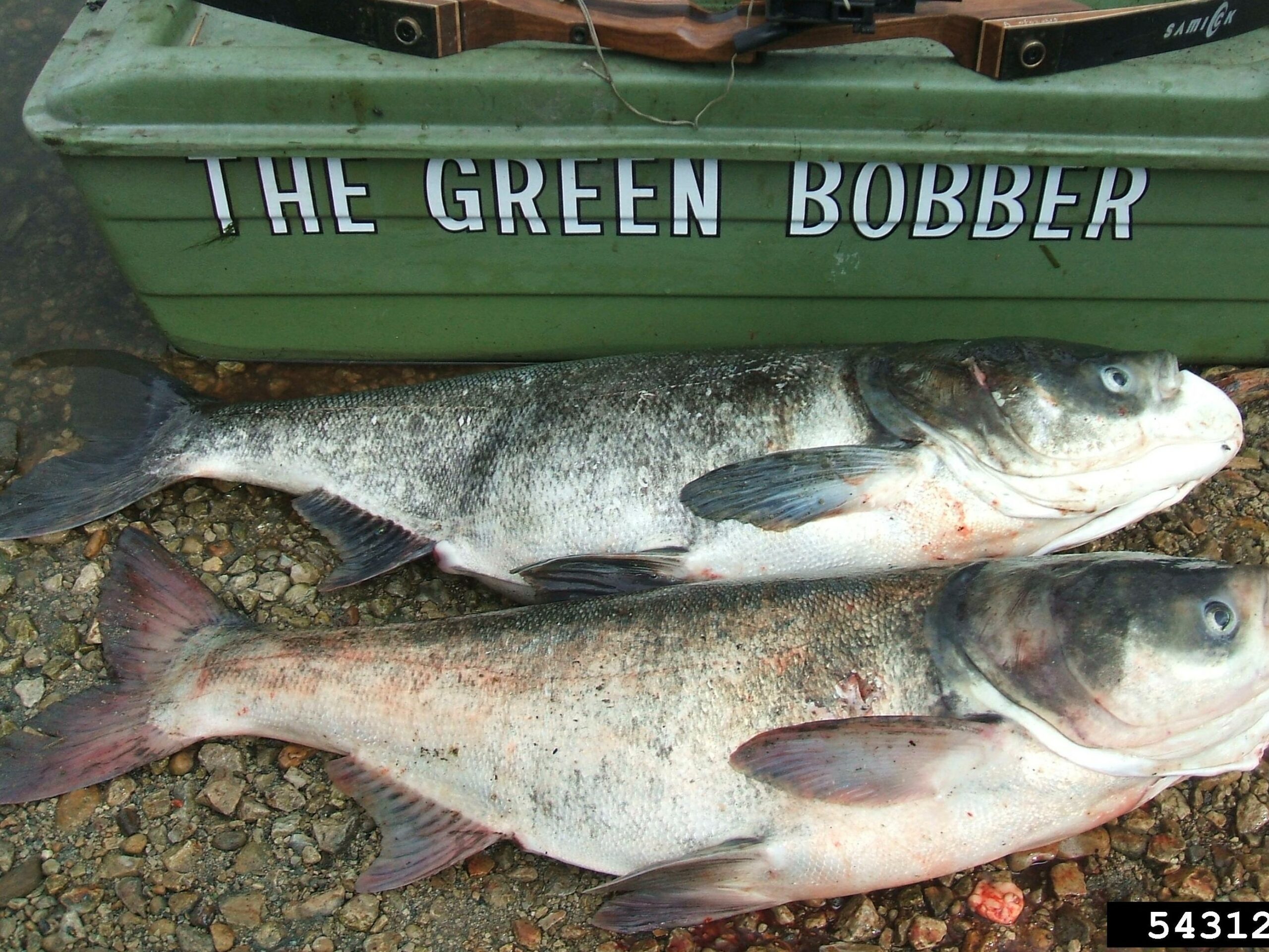

Invasive Carp
Invasive carp are a tremendous threat to the Great Lakes and could devastate the lakes if they enter

Invasive Knotweed
Two non-native invasive plants that have been gaining a foothold in recent years in Northern Michigan are Japanese

Invasive Phragmites (Common Reed)
Phragmites (Phragmites australis), also known as the common reed, is an aggressive wetland invader that grows along the
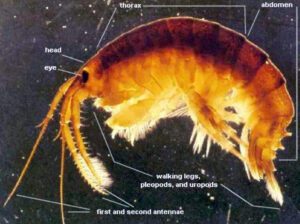
Killer Shrimp
Killer shrimp is an amphipod native to the Ponto-Caspian region that has recently invaded and spread throughout western

New Zealand Mudsnail
New Zealand mudsnails compete with other native species for food, disrupting the food chain and threaten the health

Northern Snakehead
As with many non-native and invasive species, snakehead fish have no natural predators in the United States. This

Parrot Feather
Parrot feather is an aggressive whorled aquatic plant that is similar to watermilfoils, but emergent. Its stems can

Purple Loosestrife
Purple loosestrife (Lythrum Salicaria) is an invasive wetland plant that is beautiful, but dangerous. Imported in the 1800s

Red Swamp Crayfish
Red swamp crayfish are considered invasive in Michigan because they compete aggressively with native crayfish species for food

Rock Snot (Didymo)
Rock Snot, also known as didymo, is a non-indigenous nuisance diatom. It can form large mats along the

Round Goby
Round gobies originated in the Black and Caspian Seas. They were introduced into the Great Lakes by ballast

Rusty Crayfish
Rusty Crayfish are invasive crustaceans spreading to lakes, rivers, and streams in several areas of North America. They

Spiny and Fishhook Waterflea
Spiny water fleas are tiny crustaceans that are native to Europe and Asia. They were first found in

Sea Lamprey
Sea Lamprey are primitive, jawless fish native to the Atlantic Ocean. In 1921, lampreys appeared in Lake Erie

Starry Stonewort
Starry stonewort is a submerged aquatic macroalgae with many irregular branches. It is native to Europe and was

Water Chestnut
Water chestnut forms dense mats that shade out native aquatic vegetation, leading to a decrease in biodiversity. Decomposition

Water Soldier
Dense mats of vegetation can form to crowd out native species and decrease biodiversity. Water soldier can potentially

Yellow Floating Heart
Yellow floating heart can create dense mats that shade out native aquatic plants, decrease oxygen levels, increase mosquito

Zebra Mussels and Quagga Mussels
The sheer number of zebra mussels in combination with their feeding habits has caused severe disruptions in aquatic
Resources
Michigan Invasive Species List – https://www.michigan.gov/invasives
CAKE CISMA (Charlevoix, Antrim, Kalkaska, and Emmet Cooperative Invasive Species Management Area) – https://www.cakecisma.org/
Huron Coastal Invasive Species Network – https://www.huronpines.org/hcisn
Huron Heartland Invasive Species Network – https://www.huronpines.org/hhisn
MISIN (Midwest Invasive Species Information Network) – https://www.misin.msu.edu/



