European Frogbit
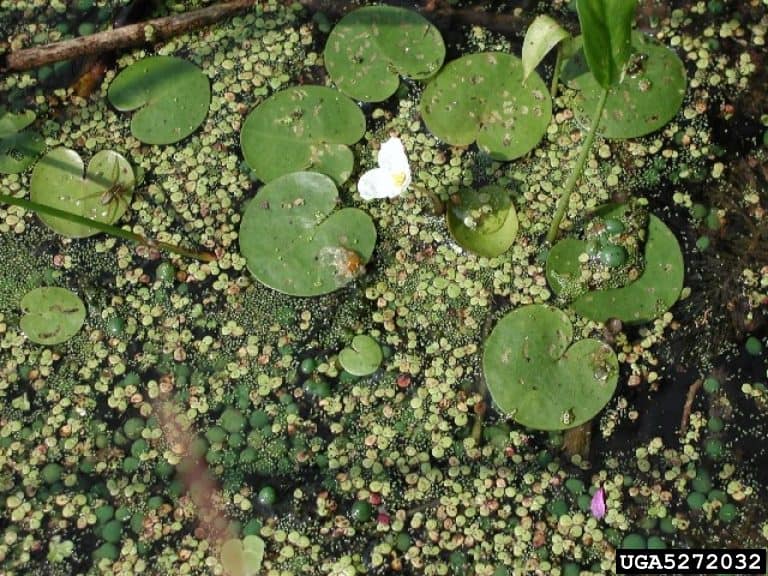

Hydrocharis morsus-ranae, better known as European Frogbit, is an aquatic, invasive species currently spreading throughout the Great Lakes Basin.
Giant Hogweed
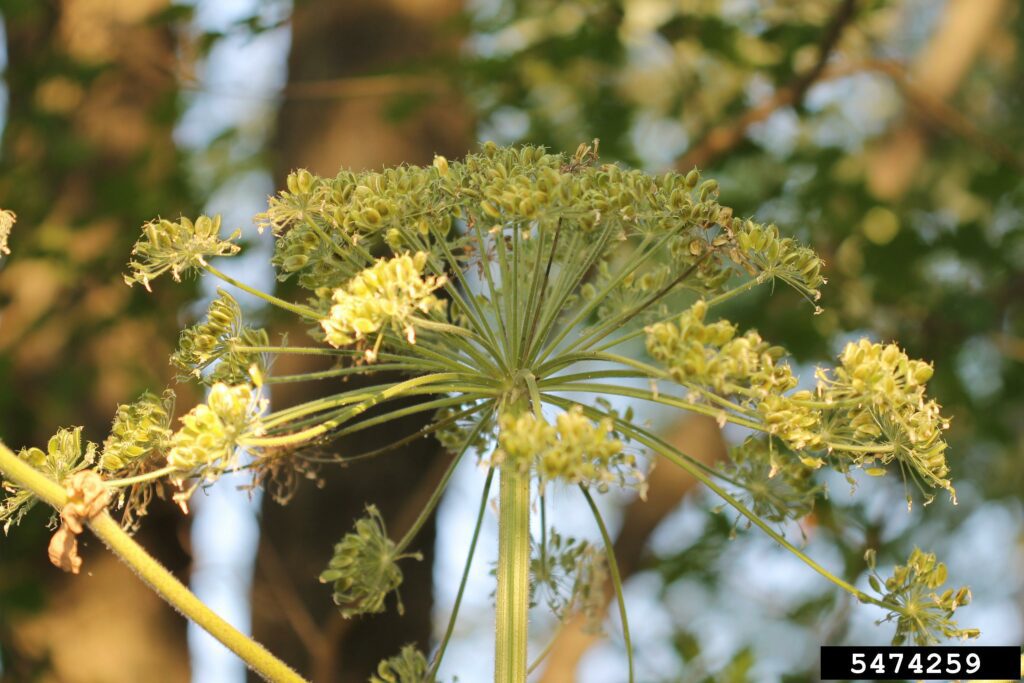

Giant Hogweed is a Federally listed noxious weed. Its sap, in combination with moisture and sunlight, can cause severe skin and eye irritation, painful blistering, permanent scarring and blindness.
Golden Mussel
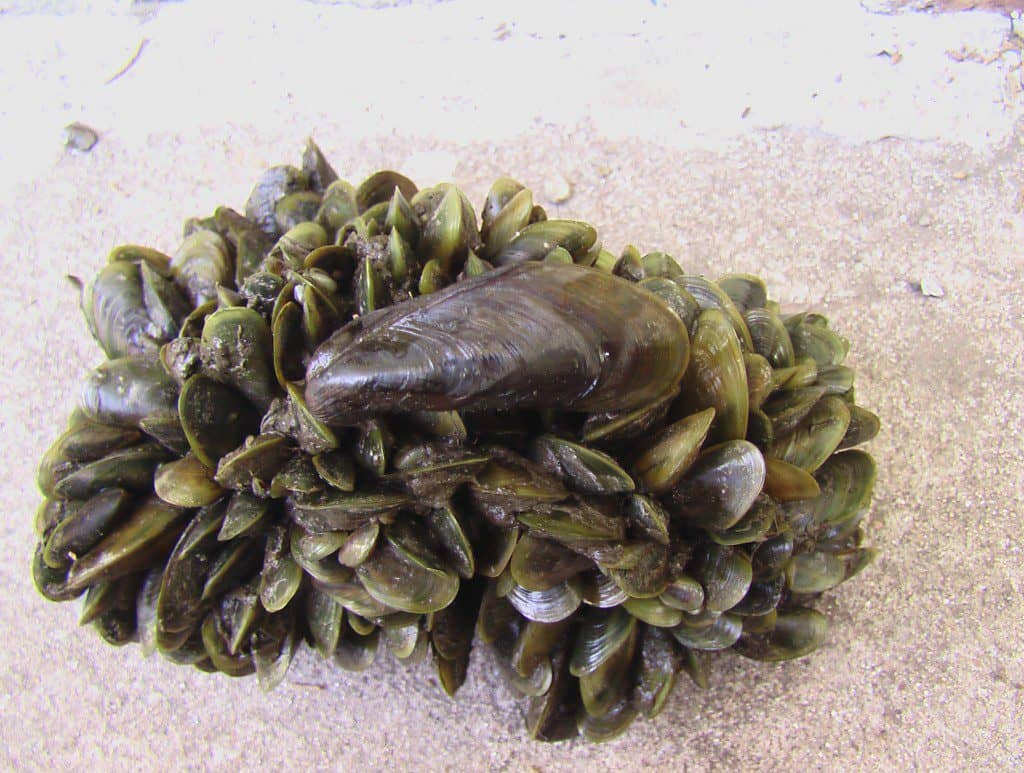

Golden Mussel is native to Chinese and south-eastern Asian rivers and creeks. It became established in Hong Kong in 1965, and in Japan and Taiwan in the 1990’s. In 1991, it invaded America through the Plata Basin in South America. Golden Mussels modify the presence and abundance of native macroinvertebrates and causes great economic damage to water intakes and cooling systems.
Invasive Knotweed
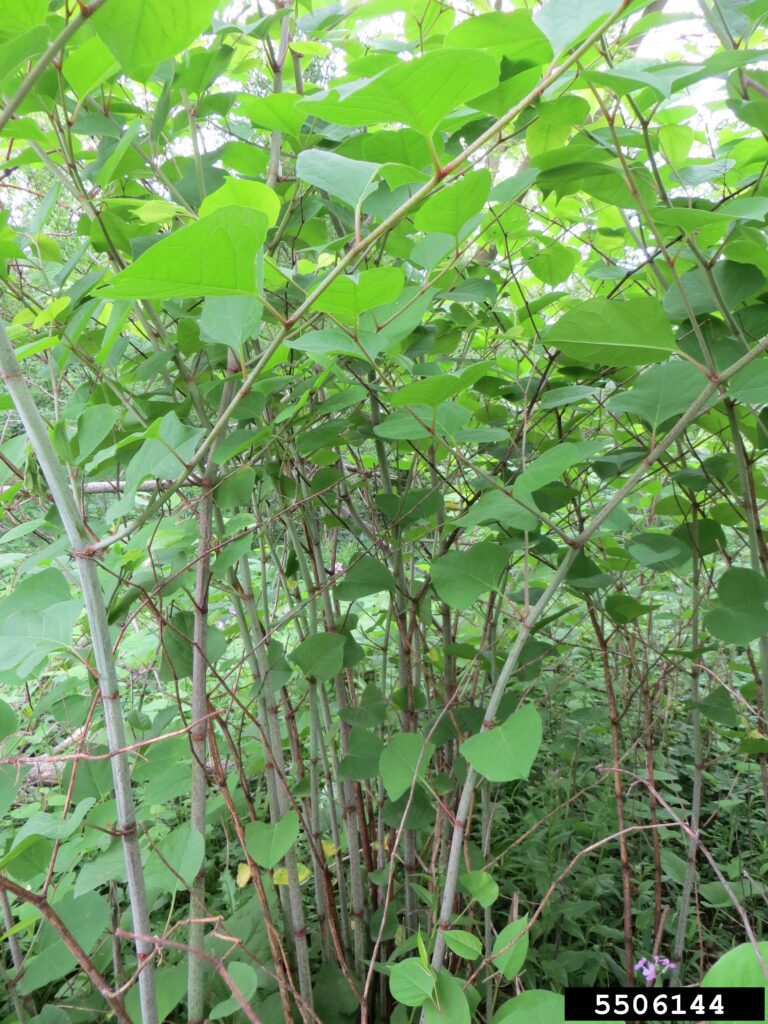

Two non-native invasive plants that have been gaining a foothold in recent years in Northern Michigan are Japanese Knotweed (Fallopia japonica) and Giant Knotweed(Fallopia sachalinensi). Both invasive species were introduced from Asia as ornamental plants.
Killer Shrimp
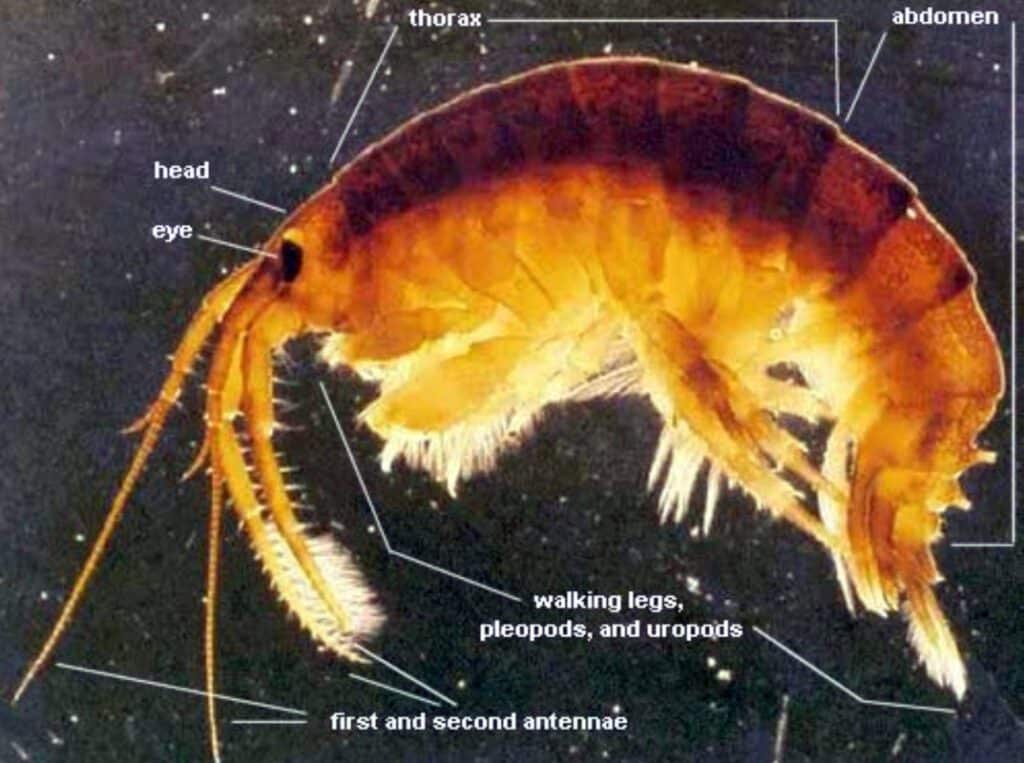
Killer shrimp is an amphipod native to the Ponto-Caspian region that has recently invaded and spread throughout western Europe. Its populations have caused in significant ecological disruption, including reduced biodiversity and local species extinction. Although not yet known in North America, there is major concern this aggressive predator could severely threaten the trophic levels of the Great Lakes by preying on a range of invertebrates.
Round Goby
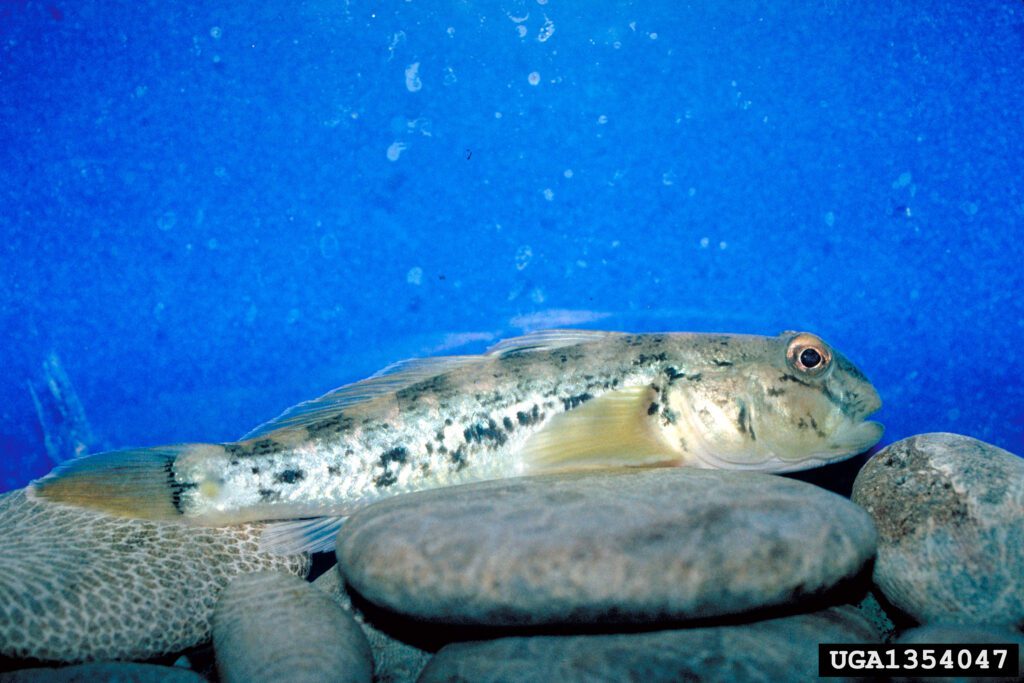

Round gobies originated in the Black and Caspian Seas. They were introduced into the Great Lakes by ballast water discharges from ships and were first discovered in 1990 along the St. Clair River (a Canadian river north of Detroit). Round gobies are a threat because of they are capable of rapid population growth after they reach new areas.
Starry Stonewort
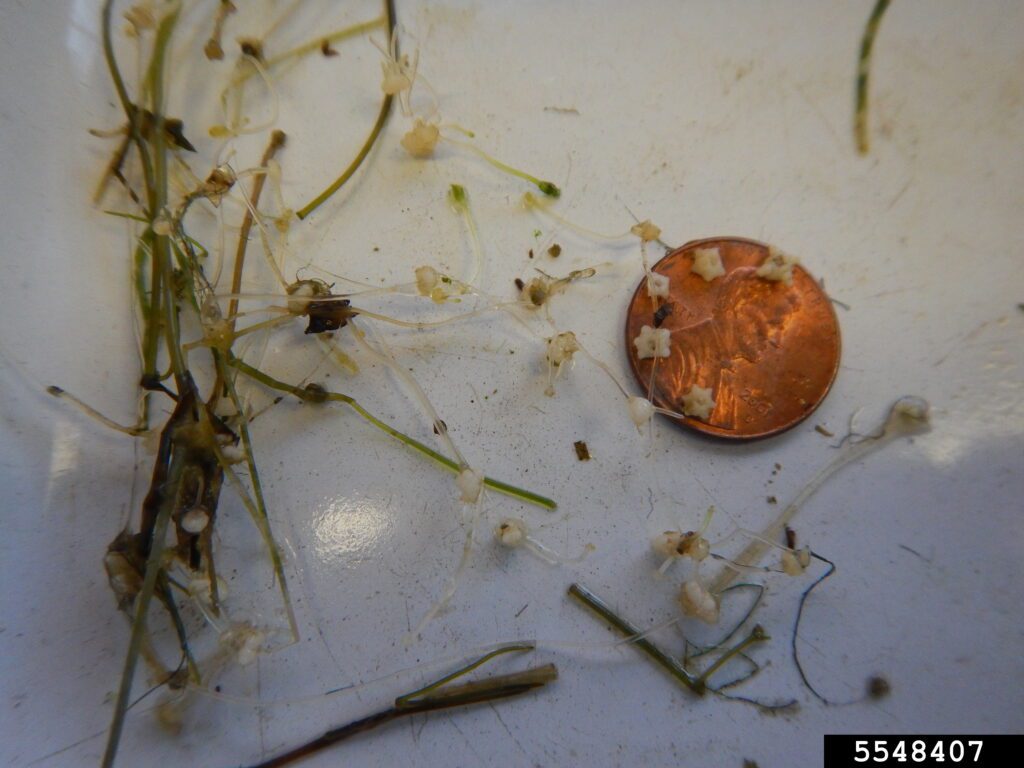

Starry stonewort is a submerged aquatic macroalgae with many irregular branches. It is native to Europe and was likely introduced in ballast water to the Great Lakes.

